这篇文章是Cartographer的理论基础,描述了一种可达到实时效果的用于激光雷达室内SLAM建图方法。目前对SLAM的学习和理解还处在一个很初级的阶段,对除文章描述方法之外的其他方法以及整个方向缺乏认知,需要以这篇文章以及Cartographer的源码阅读为契机,理解SLAM以至自动驾驶方向的任务目标、评价指标、实现方法等,深度参与到这个方向中去。
Workflow
-
lidar sensor输入一个scan,scan包含辐射状的[x, y, theta]range data和当前的位姿pose。
pose ξ = (ξy, ξx, ξθ),ξ 为scan相对其所属的submap的pose的刚性变换。
range data H = {hk}k=1,…,K,hk∈R2
-
将scan的原始数据送入voxel filter进行下采样。voxel filter讲空间分割为小的box,每个box只保留box内所有range data的质心。
-
进入local slam:迭代地将下采样后的scan与submap进行匹配,对submap进行构建。
-
对于新得到的scan,通过对scan pose与submap pose构造非线性最小二乘优化(CS),最大化scan在submap中的概率对scan的pose进行优化,得到scan插入submap的位置和角度。其中Tξ将hk从scan坐标转换到submap坐标。Msmooth为将二维的坐标数据平滑为一维的概率值数据的方法,这里采用双三次插值。cartographer中直接使用ceres-solver对(CS)进行优化,得到优化后的位姿 ξ。
\[argmin_{\xi} \sum_{k=1}^{K}(1-M_{smooth}(T_{\xi}h_{k}))^2\] -
将调整后的scan插入submap的概率grid,scan的range data在grid上表现为hit或miss。若之前概率grid上为空,hit或miss则加入。若之前概率grid不为空,则根据文章公式(2), (3)更新概率值。
-
将scan插入submap时的相对位姿relative pose保存在内存中,用以进行loop closure。
-
-
每过一个短的时间段(2s)进入global slam:将所有已完成构建的submaps和所有scans作为loop closure的约束进行sparse pose adjustment(pose optimization)。
-
思路:relative pose是使得一个scan与对应submap匹配最好的位姿,即在局部上是最优的。要进行全局优化,要使所有scan对所有submap的匹配最优。可以通过最小化relative pose与真实pose之间的残差进行优化。在窗口内通过(BBS)对所有ξ进行优化,使(SPA)最小化。
-
后台运行一个scan matcher将当前submap/scan?与历史数据进行匹配,当得到一个较高的match时,通过SPA进行回环检测,对历史所有的submap pose与scan pose进行优化。
-
优化的目标参数为(世界坐标下?)目前一构建完的所有submap的pose以及用于构建submap的所有scan的pose,Ξm与Ξs。Ξm为1,…,m的submap的pose,Ξs为1,…,n的的scan的pose。
-
优化服从的约束为Σij和ξij,Σij为submapi与scanj的协方差,ξij为submapi与scanj的相对位姿,具体为scan在submap的何处插入。
-
构造(SPA)以及(BBS)如下,得到参与优化的submap与scan的优化位姿。参与优化的submap、scan pose由scan matcher在后台搜索到的具有relative pose的submap-scan pair组成。
\[argmin_{\Xi^{m}, \Xi^{s}} \frac{1}{2}\sum_{ij}\rho(E^2(\xi_i^m,\xi_j^s;\Sigma_{ij},\xi_{ij})) \ \ (SPA)\\ \xi^*=argmax_{\xi\in W}\sum_{k=1}^KM_{nearest}(T_{\xi}h_k) \ \ (BBS)\] -
优化ξ*通过分支界限法对最优解搜索进行加速。ξ*的优化本身是连续的数值优化问题,这里通过构造成离散的空间将其转换为搜索问题,搜索窗口限定内使(BBS)最大的ξ*。具体为:窗口的大小设置为7m,由于网格的resolution为5cm,故搜索空间为上取整(W/r)=700/5=140,即x,y的搜索空间为(140*2)×(140*2)大小。
-
原始的对ξ*的优化通过对整个搜索空间穷举得到。穷举搜索空间消耗过大计算量无法满足实时,所以这里采用分支界限法对搜索树进行剪枝。实现中主要是:节点选择,分支,计算上界会影响到算法的效果。这里具体的方法还没看明白。TODO。
截图中(0, 14),(0, 15)为submap的pose,连线为与scan的constraints。
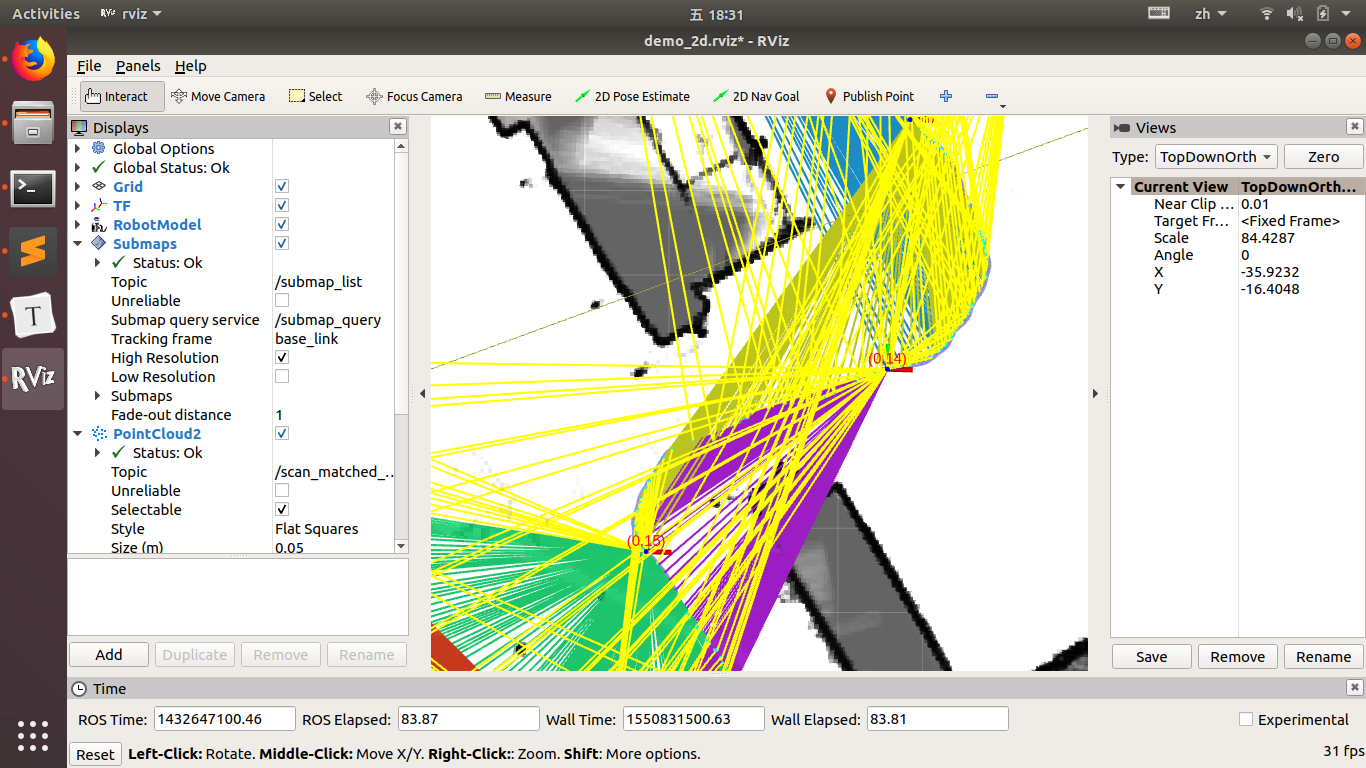
-
Basic
- grid-map,地图以grid-map的形式表示,每个grid为一个pixel,换算到世界坐标为一个5×5cm的网格。像素值表示当前grid是障碍物的概率值,通过所有邻近该grid的scan point累加得到。
- submap,结构为一个rZ×rZ的概率矩阵,值域为[0, 1]。submap的构建由多个scan迭代匹配得到,demo中 num_range_data = 90。
- scan-matching,将scan与submap M进行对齐。
- scan-pose,每个scan frame都对应一个pose ξ = (ξy, ξx, ξθ)。
- loop closure,每当新的scan的位姿与历史数据得到了较好的匹配,说明可以形成闭环,从而对全局的历史数据进行对齐。
- branch and bound approach,将非线性数值优化转换为树搜索并通过剪枝加速搜索速度。
- global与local slam都通过对pose的优化来实现。对于global slam,通过pose optimization来消除积累误差。
- scan-into-submap,将scan通过优化位姿插入submap。
- sparse pose adjustment, to optimeze the poses of all scans and submaps.
- relative pose, -
- scan matching argmin the \ksee of current scan. SPA argmin the \Ksee_m and \Ksee_s, all the submap and scan poses. relative poses for certain scan and submap \ksee_{ij} is used as constraints for SPA.
- branch and bound approach
Component
cartographer源码目录结构:
- cloud:程序对外的入口
- common:一些基本数据结构和方法的定义
- ground_truth:生成ground truth,不清楚具体功能
- io:定义数据处理和转换,以及向上向下的接口
- mapping:最主要的部分,定义submap构建及回环检测的方法
- metrics:定义用于计算时使用的指标
- pose_graph:全局位姿优化时,构建的pose graph的数据结构
- sensor:雷达和点云数据结构定义等
- transform:位姿的数据结构和相互转换的方法
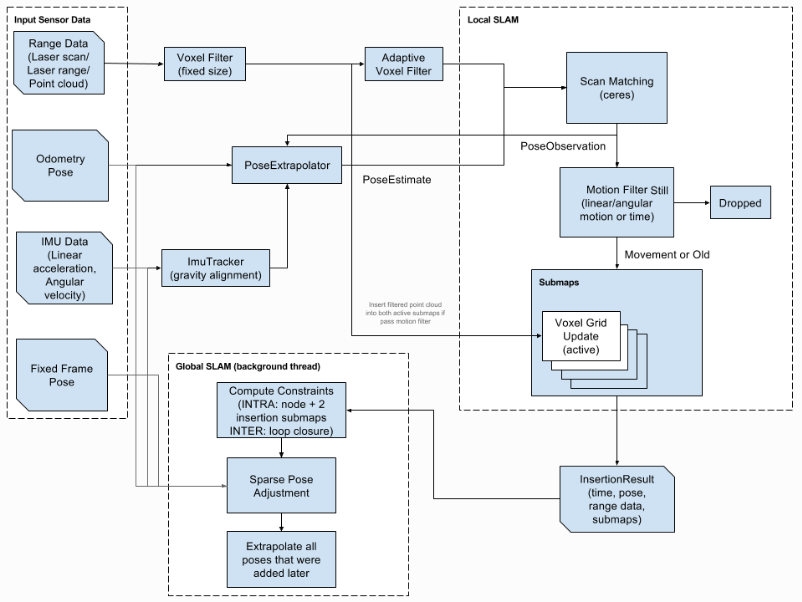
Two scan matching strategies are available:
- The CeresScanMatcher takes the initial guess as prior and finds the best spot where the scan match fits the submap. It does this by interpolating the submap and sub-pixel aligning the scan. This is fast, but cannot fix errors that are significantly larger than the resolution of the submaps. If your sensor setup and timing is reasonable, using only the CeresScanMatcher is usually the best choice to make.
- The RealTimeCorrelativeScanMatcher can be enabled if you do not have other sensors or you do not trust them. It uses an approach similar to how scans are matched against submaps in loop closure (described later), but instead it matches against the current submap. The best match is then used as prior for the CeresScanMatcher. This scan matcher is very expensive and will essentially override any signal from other sensors but the range finder, but it is robust in feature rich environments.
Trival but Important Tricks
- Submaps must be small enough so that the drift inside them is below the resolution, so that they are locally correct. On the other hand, they should be large enough to be distinct for loop closure to work properly.
Summary
- local slam与global slam,以及保持整个地图一致的intuitive:**Scan matched to submap at a short period is assumed to be sufficiently accurate. By aligning scan to submap at each short time period the map is constructed at real-time. Scan matching only happens on recent submap (at the same position of different time will form different submap). **
- loop closure中约束的直观理解:Constraints can intuitively be thought of as little ropes tying all nodes together. The sparse pose adjustement fastens those ropes altogether. The resulting net is called the “pose graph”.
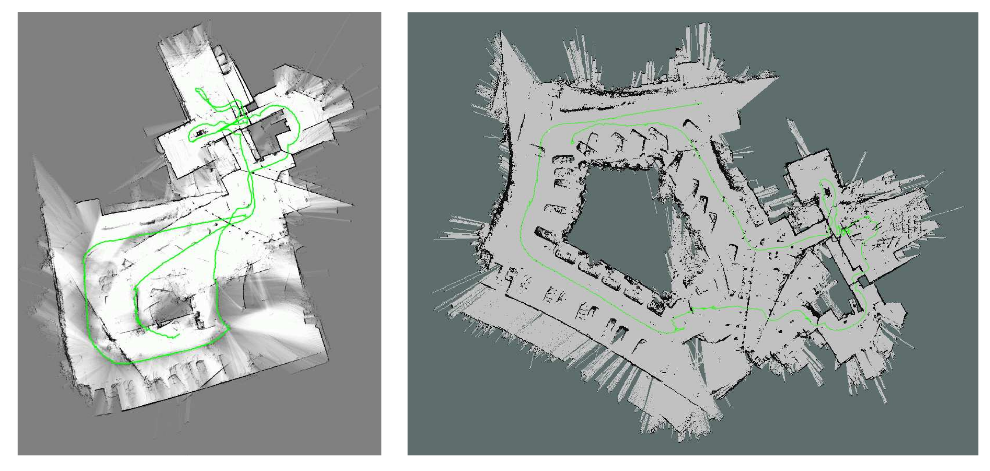
- 在特征丰富的室内场景cartographer可以得到很好的结果,但在特征稀疏的对称空间(如长的隧道)或室外效果退化比较严重。下图是一个走廊的slam建图,左侧是cartographer,右侧是hector slam的效果。(TODO,结合scan-submap-loop-closure的原理想这种情况是如何发生的)
- cartographer standalone without ROS
- Sparse Pose Adjustment SPA paper
- Branch and Bound Scan Matching BBS paper
TODOLIST
- 双三次插值对range data进行平滑的数学形式
- branch and bound approach,上界计算等
-
ceres-solver及使用
- Mnearest is M extended to all of R2 by rounding its arguments to the nearest grid point first,Mnearest没理解明白